Procedures
breast

Breast Implant
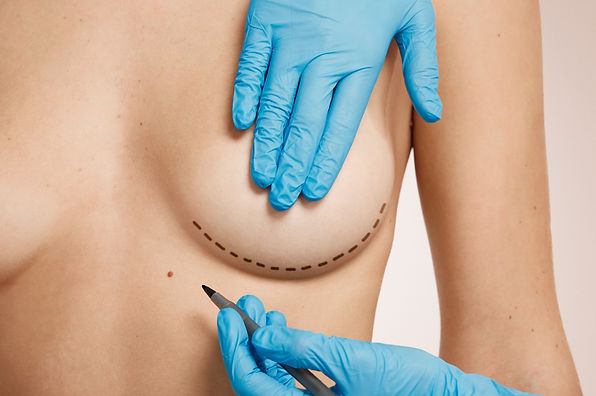
Breast augmentation is a surgical procedure designed to improve the size and shape of a person's breasts. It is usually performed with implants, which can be filled with either saline or silicone gel. The procedure begins with an incision at one of the possible sites, such as under the breast crease, around the areola, or in the armpit. The choice of incision site depends on factors such as the patient's anatomy, the desired result, and the surgeon's preferences. After making the incision, the surgeon creates a pocket either behind the breast tissue or under the pectoral muscle, which is called sub-glandular or sub-muscular placement. The chosen implant is then carefully placed in the pocket, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical adhesive.
A variety of surgical techniques are used in breast augmentation. Among the most common are:
1. Inframammary incision: in this technique, an incision is made in the breast crease where the breast meets the chest wall. It provides direct access to the implant site and allows for precise positioning.
2. Periareolar incision: in this technique, the incision is made at the edge of the areola. This incision has the advantage of being well hidden in the natural color transition of the areola.
3. Transaxillary incision: in this technique, an incision is made in the armpit and the implant is inserted and positioned using special surgical instruments. The advantage of this method is that there are no visible scars on the breasts.
The choice of surgical technique depends on several factors, including the patient's preferences, the surgeon's experience, and the specific goals of the procedure. It is important to consult a board-certified plastic surgeon who can assess individual needs and recommend the most appropriate technique to achieve the desired results.
Breast Implant
Preoperative Care for Breast Augmentation
-
Consultation: Schedule a consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon who specializes in breast augmentation. Discuss your aesthetic goals and expectations for the procedure. The surgeon will evaluate your breast anatomy, medical history, and assess whether you are a suitable candidate for surgery.
-
Communication: Clearly articulate your desired outcomes to your surgeon. Consider using visual aids, such as photographs or models, to demonstrate your expectations. Make sure you understand the potential results and any limitations associated with the procedure.
-
Medical Exam: Undergo a thorough medical examination to ensure you are in good health for surgery. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and a review of your medical history. Disclose any pre-existing conditions, allergies, or medications you are currently taking.
-
Medication Review: Provide a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are using. Some substances can increase the risk of bleeding or interact with anesthesia, requiring adjustments or cessation prior to the surgery.
-
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, it's advisable to quit well in advance of your surgery, as smoking can impede the healing process and heighten the risk of complications. Similarly, avoid alcohol consumption for a recommended period before the operation, as it may interfere with anesthesia and increase bleeding risk.
-
Preoperative Instructions: Adhere to your surgeon's specific instructions regarding fasting and any other preparations (such as wearing specific clothing) prior to your surgery. Generally, you will be asked to avoid eating or drinking for a certain period before the procedure.
Postoperative Care after Breast Augmentation
-
Recovery Environment: Set up a comfortable and supportive recovery area at home. Arrange for someone to assist you in the initial days post-surgery and ensure you have all necessary medications and supplies available.
-
Rest and Recovery: Plan for ample rest and limit physical activity as recommended by your surgeon. Avoid strenuous exercises, heavy lifting, and activities that could strain your chest. Keep your upper body elevated when resting to help minimize swelling.
-
Pain Management: Follow your surgeon's instructions regarding pain relief medications. It’s important to take prescribed pain relievers as directed and use cold compresses to manage swelling and bruising during the initial recovery.
-
Breast Care: Adhere to your surgeon’s advice for caring for your breasts post-surgery. This includes following instructions for incision care, applying prescribed ointments, and avoiding any pressure or strain on your chest during recovery.
-
Support Garments: Wear any recommended support garments or bras as instructed to provide adequate support during the healing process. This can help reduce swelling and provide comfort.
-
Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. These check-ups are crucial for monitoring your recovery, removing sutures if necessary, and addressing any questions or complications you may encounter during the healing process.
It is vital to closely follow your surgeon's pre-and post-operative instructions to ensure a successful recovery and optimal surgical results. If you have any questions or concerns during your recovery, reach out to your surgeon promptly for guidance.
Breast Lift
Breast lift, also called mastopexy, is a cosmetic procedure performed to lift and reshape sagging breasts. This is to correct problems such as ptosis (sagging), loss of breast volume and nipple position. Below is some information about breast lift and the techniques involved:
Evaluation and Planning:
During the initial consultation, a board-certified plastic surgeon will examine your breasts, discuss your goals and expectations, and evaluate your overall health and medical history. The surgeon will determine the most appropriate technique based on factors such as the degree of breast sagging, nipple position, and breast volume.
Types of incisions:
There are several types of incisions used in breast lift surgery:
a. Peri-areolar incision: this incision is made around the areola (the dark skin surrounding the nipple). It is suitable for people with mild to moderate breast sagging.
b. Vertical incision: in addition to the periareolar incision, a vertical incision is made that extends from the underside of the areola to the crease under the breast. This technique is suitable for moderately to severely sagging breasts.
c. Anchor incision: this technique involves a periareolar incision, a vertical incision, and a horizontal incision along the crease of the breast. It is used in individuals with severe breast sagging.
Breast Lift
Reshaping the breast tissue:
After making the necessary incisions, the surgeon reshapes the breast tissue to lift and tighten the breasts. This involves moving the underlying breast tissue to a higher position, removing excess skin and tightening the remaining skin.
Repositioning of nipples and areola:
If the nipples sit lower on the breasts, they are brought to a more youthful height. The surgeon may also adjust the size of the areolas to achieve better symmetry and proportion.
Breast Augmentation with Lift:
In some cases, a breast lift can be combined with breast augmentation with implants to improve the size and shape of the breasts. This is an option for individuals who desire both a lift and volume augmentation.
Closure of incisions:
The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical staples. The surgeon will place bandages or dressings over the incisions, and a supportive bra or compression garment may be recommended to promote healing.
Breast Lift
Recovery and results:
Swelling, bruising and discomfort may occur after breast lift surgery. Pain medication, cold compresses, and wearing a supportive bra as directed can help relieve these postoperative effects. It is important to follow your surgeon's postoperative care instructions.
The initial results of a breast lift are visible after the swelling subsides, but it may take several weeks or months to see the final results as the breasts settle and the incision lines fade. The procedure can result in tightened, firmer breasts with improved shape, symmetry and nipple position.
During the recovery period, it is important that you avoid strenuous activity and lifting heavy objects. Follow your surgeon's instructions regarding resuming normal activities, wearing supportive bras and caring for the incision sites.
It is important that you consult with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast lift surgery to discuss your goals, understand the technique recommended for your situation, and receive personalized advice and guidance throughout the process. The surgeon will provide detailed pre- and post-operative instructions to optimize your recovery and help you achieve the results you desire.
Preoperative care for candidates preparing for a breast lift includes several important steps:
1. Consultation: schedule a consultation with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast lift procedures. During the consultation, discuss your goals, expectations and medical history. The surgeon will examine your breasts, assess your overall health and determine if you are a candidate for the procedure.
2. Medical Exam: You will undergo a comprehensive medical exam to ensure you are in good health for the procedure. This may include blood tests, imaging tests, and other diagnostic tests as determined by your surgeon. Tell your surgeon about any pre-existing conditions, allergies or medications you are currently taking.
3. Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, it is important that you stop smoking well in advance of your surgery. Smoking can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Also avoid drinking alcohol for a recommended period of time before surgery, as it can interfere with anesthesia and increase the risk of bleeding.
4. Medication review: provide your surgeon with a complete list of medications, supplements and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications and supplements may increase the risk of bleeding or interact with anesthesia, so your surgeon may advise you to stop or adjust them before surgery.
5. Preoperative instructions: Follow your surgeon's instructions about fasting before your procedure. You will usually be asked not to eat or drink anything for a certain amount of time before the procedure.
Breast Lift
Postoperative care after a breast lift is critical for optimal healing and recovery. Here are some general guidelines:
1. Recovery facility: provide a comfortable and supportive recovery environment. This includes having someone available to assist you in the first few days after surgery and having necessary medications and supplies handy.
2. Rest and recovery: plan for adequate rest and downtime after surgery. Avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects during the initial recovery period. It is important to elevate your chest when sleeping to minimize swelling and promote healing.
3. Pain management: take pain medications as prescribed by your surgeon to relieve discomfort and pain during the initial recovery period. Use cold compresses as recommended to reduce swelling and bruising.
4. Supportive bra: Your surgeon may recommend that you wear a supportive bra or compression garment after surgery to support your breasts and aid in healing. Follow your surgeon's instructions about what type of bra to wear and how long to wear it.
5. Care of the wound: Follow your surgeon's instructions for caring for your incisions. Keep the incision areas clean and dry and apply any ointments or dressings prescribed. Avoid excessive sun exposure and protect your incisions from direct sunlight.
6. Follow-up appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. At these appointments, your surgeon can monitor your healing progress, remove any sutures or staples, and address any concerns or complications.
It is important that you follow your surgeon's pre-and post-operative instructions carefully for a successful recovery and optimal results. Contact your surgeon if you have any questions or concerns during the recovery period. He or she will provide specific advice tailored to your individual needs and monitor your progress throughout the recovery process.

Breast Reduction
Breast reduction, also called mammareductionplasty, is a surgical procedure aimed at reducing and reshaping breasts. It is primarily performed to relieve physical discomfort, improve breast proportions, and enhance overall well-being. Below you will find some information about breast reduction and the techniques used in the process:
Examination and Planning:
During the initial consultation, a plastic surgeon specializing in breast reduction will evaluate your breasts, discuss your concerns and goals, and assess your overall health and medical history. The surgeon will determine the most appropriate technique based on factors such as breast size, shape, degree of sagging, and nipple position.
Types of incisions:
There are several types of incisions used in breast reduction, depending on the desired result and the amount of excess breast tissue to be removed:
a. Anchor incision or inverted-T incision: in this technique, an incision is made that surrounds the areola, extends vertically downward from the areola to the breast crease, and then runs horizontally along the breast crease. It is suitable for people with larger breasts and severe sagging.
b. Vertical incision or lollipop incision: in this technique, an incision is made around the areola and a vertical incision is made from the areola to the breast crease. It is suitable for people with medium sized breasts and moderate sagging.
c. Peri-areolar incision: in this technique, the incision is made only around the areola. It is suitable for people with smaller breasts and mild to moderate sagging.
Breast Reduction
Breast tissue removal and reshaping:
After making the necessary incisions, the surgeon removes excess breast tissue, fat and skin. The remaining breast tissue is reshaped and lifted to create a more proportional and esthetic breast contour. The nipples and areolas may also be raised to a higher position for a more youthful appearance.
Liposuction:
In some cases, liposuction may be performed in conjunction with breast reduction to remove excess fat from the sides of the breasts or underarm area to create better contouring and symmetry.
Closure of incisions:
Incisions are closed with sutures or surgical staples. The surgeon places bandages or dressings over the incisions, and a supportive bra or compression garment may be recommended to aid in healing.
Recovery and results:
Swelling, bruising and discomfort may occur after a breast reduction. Pain medication, cold compresses, and wearing a supportive bra as directed can help alleviate these post-operative effects. It is important to follow your surgeon's postoperative care instructions.
The initial results of breast reduction are visible after the swelling subsides, but it may take several weeks or months to see the final results as the breasts heal and firm up. The procedure can result in reduced breast size, improved breast shape and symmetry, relief from physical discomfort, and an overall more balanced and proportional appearance.
During the recovery period, you should avoid strenuous activity and lifting heavy objects. Follow your surgeon's instructions regarding resuming normal activities, wearing supportive bras, and caring for the incision sites.
It is important that you consult with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast reduction to discuss your goals, understand the technique recommended for your situation, and receive personalized advice and guidance throughout the process. The surgeon will provide detailed pre-and post-operative instructions to optimize your recovery and help you achieve your desired results.

Breast Reduction
Preoperative care for candidates preparing for breast reduction surgery includes several important steps:
Consultation: schedule a consultation with a plastic surgeon who specializes in breast reduction surgery. During the consultation, discuss your goals, concerns and medical history. The surgeon will examine your breasts, assess your overall health and determine if you are a candidate for the procedure.
Medical Exam: You will undergo a comprehensive medical exam to ensure you are in good health for the procedure. This may include blood tests, imaging tests, and other diagnostic tests as determined by your surgeon. Inform your surgeon of any pre-existing conditions, allergies or medications you are currently taking.
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, it is important that you stop smoking well in advance of your surgery. Smoking can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Also avoid drinking alcohol for a recommended period of time before surgery, as it can interfere with anesthesia and increase the risk of bleeding.
Medication review: provide your surgeon with a complete list of medications, supplements and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications and supplements may increase the risk of bleeding or interact with anesthesia, so your surgeon may advise you to stop or adjust them before surgery.
Preoperative instructions: Follow your surgeon's instructions about fasting before your procedure. You will usually be asked not to eat or drink anything for a certain amount of time before the procedure.

Breast Reduction
Postoperative care after breast reduction is critical for optimal healing and recovery. Here are some general guidelines:
Recovery facility: provide a comfortable and supportive recovery environment. This may include having someone available to assist you in the first few days after surgery and having necessary supplies and medications handy.
Rest and recovery: plan for plenty of rest and downtime after surgery. Avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects during the initial recovery period. It is important to elevate your chest when sleeping to minimize swelling and promote healing.
Pain management: take pain medications as prescribed by your surgeon to relieve discomfort and pain during the initial recovery period. Use cold compresses as recommended to reduce swelling and bruising.
Supportive bra: Your surgeon may recommend that you wear a supportive bra or compression garment after surgery to support your breasts and aid in healing. Follow your surgeon's instructions about what type of bra to wear and how long to wear it.
Care of the wound: Follow your surgeon's instructions for caring for your incisions. Keep the incision areas clean and dry and apply any ointments or dressings prescribed. Avoid excessive sun exposure and protect your incisions from direct sunlight.
Follow-up appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. At these appointments, your surgeon can monitor the healing progress, remove any sutures or staples, and address any concerns or complications.
It is important that you follow your surgeon's pre- and post-operative instructions closely for a successful recovery and optimal results. Contact your surgeon if you have any questions or concerns during the recovery period. He or she will provide specific advice tailored to your individual needs and monitor your progress throughout the recovery process.

Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia surgery is a procedure to reduce and improve the appearance of enlarged male breasts. It is often caused by hormonal imbalances, excessive fat deposits or enlargement of the glandular tissue. Below is some information about gynecomastia surgery and the techniques used in the process:
Evaluation and Planning:
During the initial consultation, a plastic surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia surgery will examine your breasts, discuss your concerns and goals, and evaluate your overall health and medical history. The surgeon will determine the most appropriate technique based on factors such as the extent of breast augmentation, the amount of excess fat or glandular tissue, and the presence of sagging skin.
Liposuction:
In cases where gynecomastia is primarily due to excess fatty tissue, liposuction alone may be sufficient. This involves making small incisions and suctioning out the excess fat with a thin tube (cannula). This technique can be used to reduce breast size and improve contour.
Excision:
If glandular tissue or excess skin is present, surgical removal may be necessary. In this technique, incisions are made around the areola or in the natural folds of the breast to remove the excess tissue. The surgeon may also reposition the nipple to a more esthetically pleasing position.
Combined technique:
In some cases, a combination of liposuction and excision may be used to achieve optimal results. This method removes both excess fat and glandular tissue while correcting sagging skin.

Gynecomastia
Closure of incisions:
Incisions are closed with sutures or surgical adhesive. The surgeon may use absorbable sutures that do not need to be removed. Dressings or compression garments may be applied to support the chest area and promote healing.
Recovery and outcomes:
Swelling, bruising and discomfort may occur after gynecomastia surgery. Pain medication, cold compresses, and wearing a compression garment as instructed can help relieve these postoperative effects. It is important to follow your surgeon's postoperative care instructions.
The initial results of gynecomastia surgery are visible after the swelling subsides, but it may take several weeks or months to see the final results as the breast heals and firms up. The procedure can result in a flatter, firmer and more masculine breast contour.
During the recovery period, you should avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting for several weeks. Follow your surgeon's instructions for resuming normal activities, wearing compression garments and caring for the incisions.
It is important that you consult with a plastic surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia surgery to discuss your goals, understand the technique recommended for your situation, and receive personalized advice and guidance throughout the process. The surgeon will provide detailed pre- and post-operative instructions to optimize your recovery and help you achieve your desired results.
Gynecomastia
Preoperative instructions: Follow your surgeon's instructions about fasting before your procedure.
Consultation: schedule a consultation with a plastic surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia surgery. During the consultation, discuss your concerns, goals and medical history. The surgeon will examine your breasts, assess your overall health and determine if you are a suitable candidate for the procedure.
Medical Exam: You will undergo a comprehensive medical exam to ensure you are in good health for surgery. This may include blood tests, imaging tests, and other diagnostic tests as determined by your surgeon. Inform your surgeon of any pre-existing conditions, allergies or medications you are currently taking.
Smoking and Alcohol: If you smoke, it is important that you stop smoking well in advance of your surgery. Smoking can interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications. Also avoid drinking alcohol for a recommended period of time before surgery, as it can interfere with anesthesia and increase the risk of bleeding.
Medication review: provide your surgeon with a complete list of medications, supplements and herbal remedies you are taking. Some medications and supplements may increase the risk of bleeding or interact with anesthesia, so your surgeon may advise you to stop or adjust them before your procedure.
Gynecomastia
Postoperative Care after Gynecomastia Surgery
You will usually be asked not to eat or drink anything for a certain amount of time before the procedure.
Postoperative care after gynecomastia surgery is critical for optimal healing and recovery. Here are some general guidelines:
Recovery facility: provide a comfortable and supportive recovery environment. This may include having someone available to assist you in the first few days after surgery and having necessary supplies and medications handy.
Rest and recovery: plan for plenty of rest and downtime after surgery. Avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects during the initial recovery period. It is important to elevate your chest when sleeping to minimize swelling and promote healing.
Pain management: take pain medications as prescribed by your surgeon to relieve discomfort and pain during the initial recovery period. Use cold compresses as recommended to reduce swelling and bruising.
Compression garment: your surgeon may give you a compression garment to wear after surgery. This garment helps minimize swelling, supports the chest area, and aids in the healing process. Follow your surgeon's instructions regarding how long and how often to wear the garment.
Care of the wound: Follow your surgeon's instructions for caring for your incisions. Keep the incision areas clean and dry and apply any prescribed ointments or dressings. Avoid excessive sun exposure and protect your incisions from direct sunlight.
Follow-up appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon. At these appointments, your surgeon can monitor the healing progress, remove any sutures or staples, and address any concerns or complications.
It is important that you follow your surgeon's pre- and post-operative instructions carefully for a successful recovery and optimal results. Contact your surgeon if you have any questions or concerns during the recovery period. He or she will provide specific advice tailored to your individual needs and monitor your progress throughout the recovery process.

Mastectomy
Female-to-male mastectomy (FTM), also known as "top surgery" is a gender reassignment surgery in which breast tissue is removed to create a more masculine breast. Here are some details about FTM mastectomy, including information about techniques:
Surgical Techniques:
a. Double incision mastectomy: This is the most commonly used technique for mastectomy for FTM. A horizontal incision is made across the breast, usually just below the pectoral muscles, and the breast tissue is removed. The nipple-areolar complex is usually reduced in size and repositioned to create a more masculine appearance.
b. Periareolar or keyhole mastectomy: This technique is appropriate for individuals with smaller breasts or minimal excess skin. It involves making a smaller incision around the areola to remove breast tissue. This technique is less invasive, but may not be suitable for candidates with larger breasts or severe skin sagging.
c. Inverted-T or Anchor Mastectomy: This technique is used for those with larger breasts or more excess skin. It involves making an incision around the areola that runs vertically across the breast and making an additional horizontal incision in the inframammary fold. This allows more breast tissue and excess skin to be removed.
Surgical considerations:
a. Anesthesia: FTM mastectomy is usually performed under general anesthesia to ensure the patient's comfort throughout the procedure.
b. Incision placement: the surgeon carefully plans the placement of the incisions to achieve the desired esthetic result while minimizing visible scarring. Incisions are usually placed so that they can be hidden under clothing or in the natural folds of the breast.
c. Repositioning of the nipple and areola: The surgeon may alter the size and position of the nipple-areolar complex to achieve a more masculine appearance. This involves relocating the nipples to a more appropriate position on the breast.
Mastectomy
Recovery and Healing:
a. Dressings and compression garments: After surgery, the breast is usually wrapped with bandages or compression garments to support it and minimize swelling. These may be replaced or adjusted during the recovery period.
b. Swelling and bruising: Swelling and bruising in the chest area is normal after surgery and will subside with time. Applying cold compresses and elevating the chest can help reduce swelling.
c. Pain management: pain medications may be prescribed to treat postoperative discomfort. It is important that you take the prescribed medications and inform the treatment team of any pain or concerns.
d. Activity Restrictions: During the initial recovery period, candidates must avoid strenuous activity and heavy lifting. The surgeon will provide guidelines on when it is safe to resume regular activities and exercise.
e. Follow-up visits: Regular follow-up visits with the surgical team are necessary to monitor healing progress, remove any sutures or drains, assess surgical outcomes, and address any concerns or complications.
Results:
Final results of FTM mastectomy include a flatter, more masculine breast contour. Scarring fades over time, but may still be visible, although it is often inconspicuous and can be hidden by clothing.
Candidates considering an FTM mastectomy should consult a qualified plastic surgeon who specializes in gender reassignment surgery. The surgeon will assess breast anatomy, discuss goals and expectations, and recommend the most appropriate technique based on individual circumstances. It is important to have realistic expectations and be aware that results may vary from individual to individual.
Mastectomy
The preoperative and postoperative care of candidates undergoing FTM mastectomy plays a critical role in a successful procedure and smooth recovery. Below is some information about pre- and post-operative care for individuals considering FTM mastectomy:
Pre-operative care:
Consultation and Evaluation: Candidates should schedule a consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon who has experience with gender reassignment procedures. During the consultation, the surgeon will assess the candidate's overall health, discuss her goals and expectations, and determine the most appropriate surgical technique.
Medical Exam: A comprehensive medical examination will be performed to assess the candidate's general health and suitability for surgery. This may include blood tests, imaging studies, and consultations with other specialists as needed.
Hormonal therapy: if the candidate is undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT) as part of gender reassignment, the surgeon and endocrinologist may work together to optimize hormone levels prior to surgery. Adjustment of hormone dosage or schedule may be recommended to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal surgical outcomes.
Smoking and alcohol cessation: Candidates are advised to stop smoking and abstain from alcohol for a period of time before and after surgery, as this may interfere with the healing process and increase the risk of complications.
Mastectomy
Postoperative care:
Dressings and compression garments: After an FTM mastectomy, bandages or compression garments are applied to the breast area to support the breast, minimize swelling and promote healing. These may need to be worn for several weeks as directed by the surgeon.
Swelling and bruising: Swelling and bruising are normal after surgery and will subside with time. Applying cold compresses and elevating the chest can help reduce swelling. The surgeon may also recommend special techniques or medications to reduce swelling.
Pain management: pain medications are prescribed to relieve postoperative discomfort. It is important that you take the prescribed medications and inform the treatment team of any pain or concerns.
Activity Restrictions: During the initial recovery period, candidates should avoid strenuous activity, heavy lifting and certain arm movements. The surgeon will provide specific guidelines on when it is safe to resume regular activities and exercise.
Wound care and scar management: the surgeon will provide instructions on how to care for surgical incisions and minimize scarring. This may include keeping the incisions clean and dry, applying topical ointments or silicone sheets, and keeping the incisions out of the sun.
Emotional support: the FTM mastectomy is an important step in the gender transition journey. Emotional support from friends, family, support groups or mental health professionals can be very helpful during the recovery process.
Follow-up visits: Regular follow-up visits with the surgical team are necessary to monitor healing progress, remove sutures or drains, assess surgical outcomes, and address any concerns or complications. The frequency of follow-up visits may vary depending on individual circumstances.
Healing and Recovery: Complete healing and final results from FTM mastectomy may take several weeks to months. It is important to follow the surgeon's instructions regarding postoperative care, including proper wound care, wearing compression garments as directed, and attending follow-up appointments.
It is important to communicate openly with the surgical team and follow their instructions for preoperative and postoperative care. This helps to achieve optimal outcomes, minimize risks, and promote a smooth recovery process. Pre- and post-operative care can be tailored to individual needs and the specific techniques used during the procedure.

